Dissertation Project
Spatial-Temporal Traffic Accident Analysis in relation to EMS Response Time
Abstract
Traffic accidents constitute one of the dominant causes of death globally, influencing the welfare of modern society significantly. Aberdeen City is considered as one of the most traffic-congested cities in the UK, resulting in more than 180 incidents per year for the last 10-year period. The purpose of this study is to perform an accidents cluster analysis in the City of Aberdeen by examining both time and space aspects in relation to the Emergency Medical Services (EMS) response time. Performing network cluster analysis, new space-time accident hot spots are detected on the road network and then a composite examination between those hot spots and the EMS response time is performed.
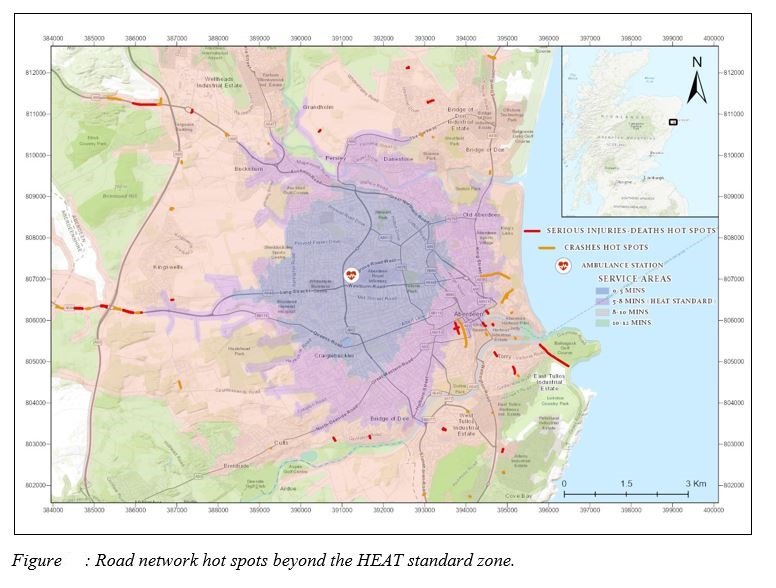
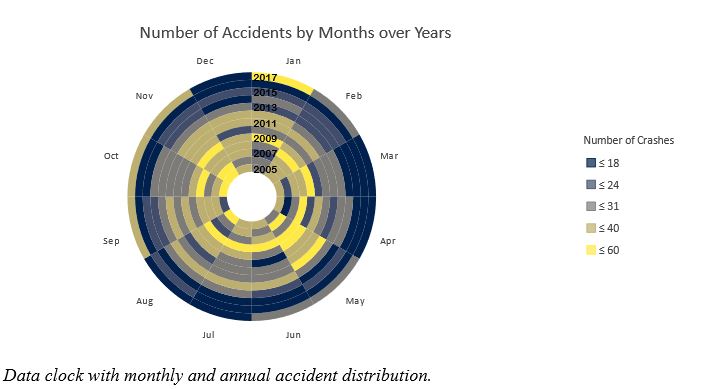
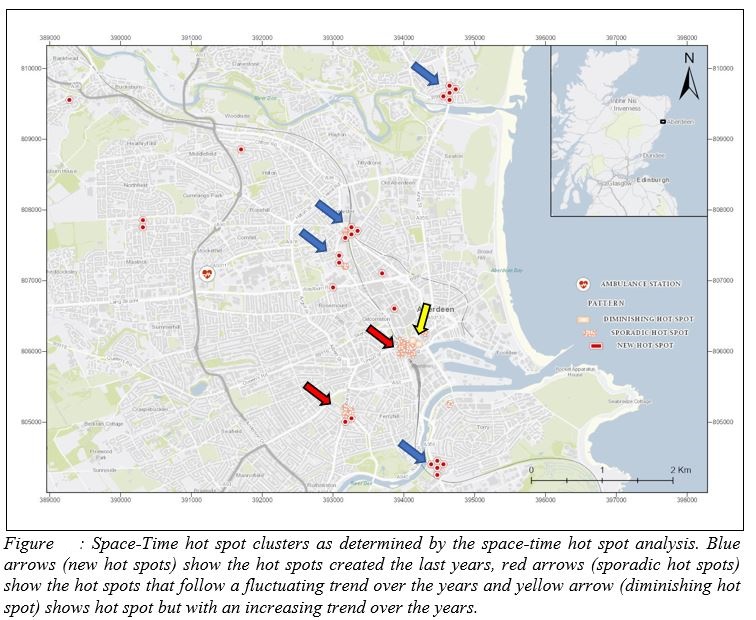
Throughout the performed analysis and examination of the traffic accident data, some new accident trends have been identified, during the last few years. Moreover, a high density of accidents takes place during specific day hours and months. Finally, most of the hot spots are located within the boundaries of the HEAT standard of 8 minutes, constituting the EMS station ideally situated. However, an emphasis should be given on those hot spots located farther than the 8-minutes zones, and further policies should be deployed against those prone areas.
Methodology
1. Data Preparation
Data cleansing and validation is achieved so that data to be ready for use by the GIS software. The datasets contain information about traffic accidents in the UK, the road network and the location of the ambulance station. Afterwards, the data are analysed in a spatial-temporal framework revealing interesting space-time patterns.
- Study Area
- Data Acquisition
2. Road Network Analysis
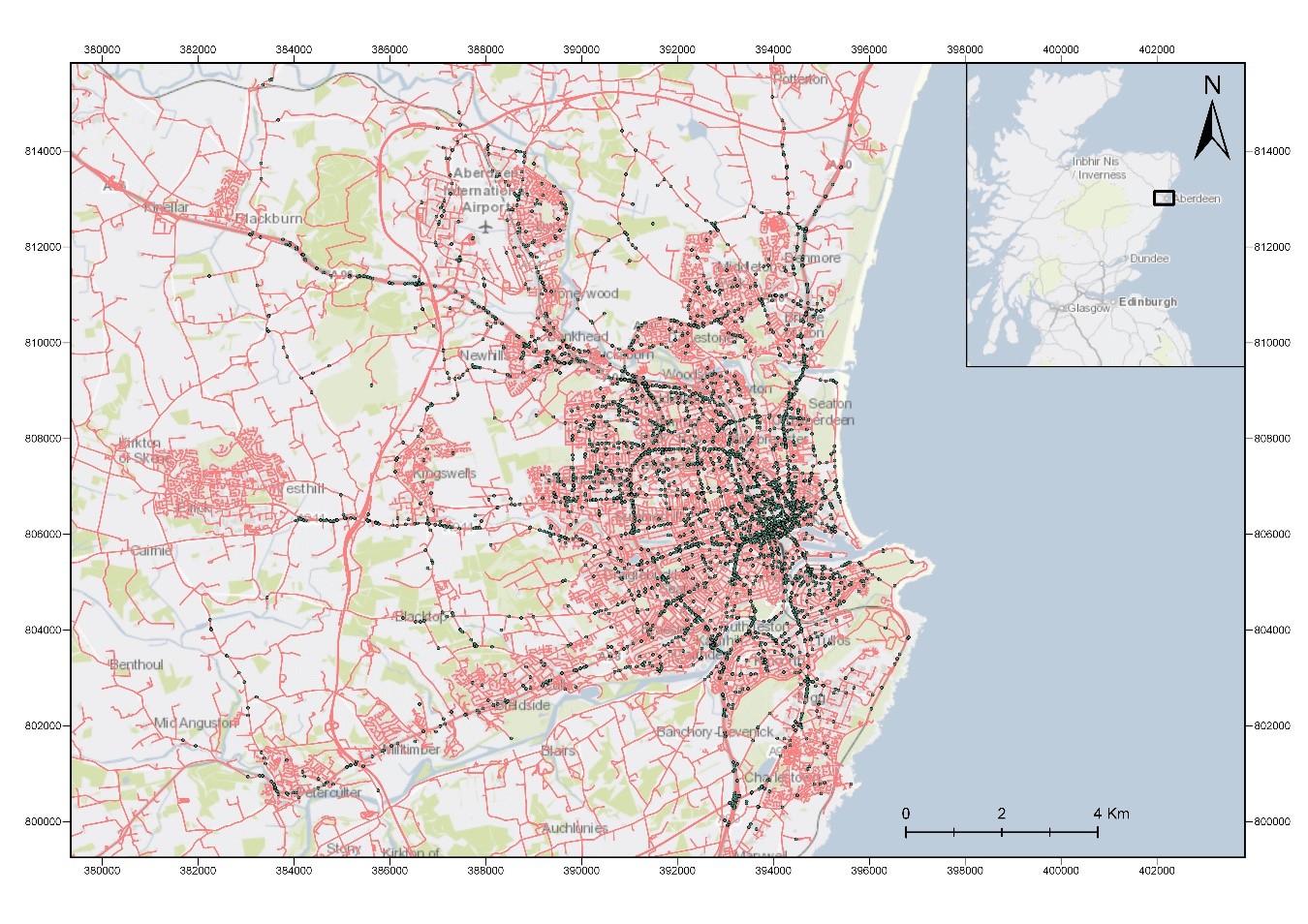
The road network dataset which is acquired with a UK national coverage, contains information on virtually every road segment across the UK. The road network was clipped into the extent of the boundaries of Aberdeen city in order to make the data manipulation easier and faster.
- EMS Response Time Distribution
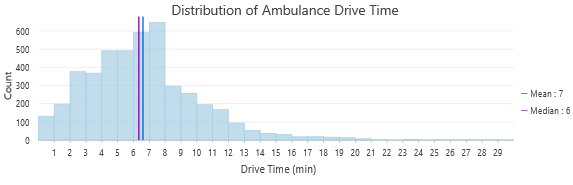 The ‘Find Closest Facility’ tool was used to calculate the Distribution
The ‘Find Closest Facility’ tool was used to calculate the Distribution -
Space-time patterns and Emerging Hot spots
 Used Tools
Used Tools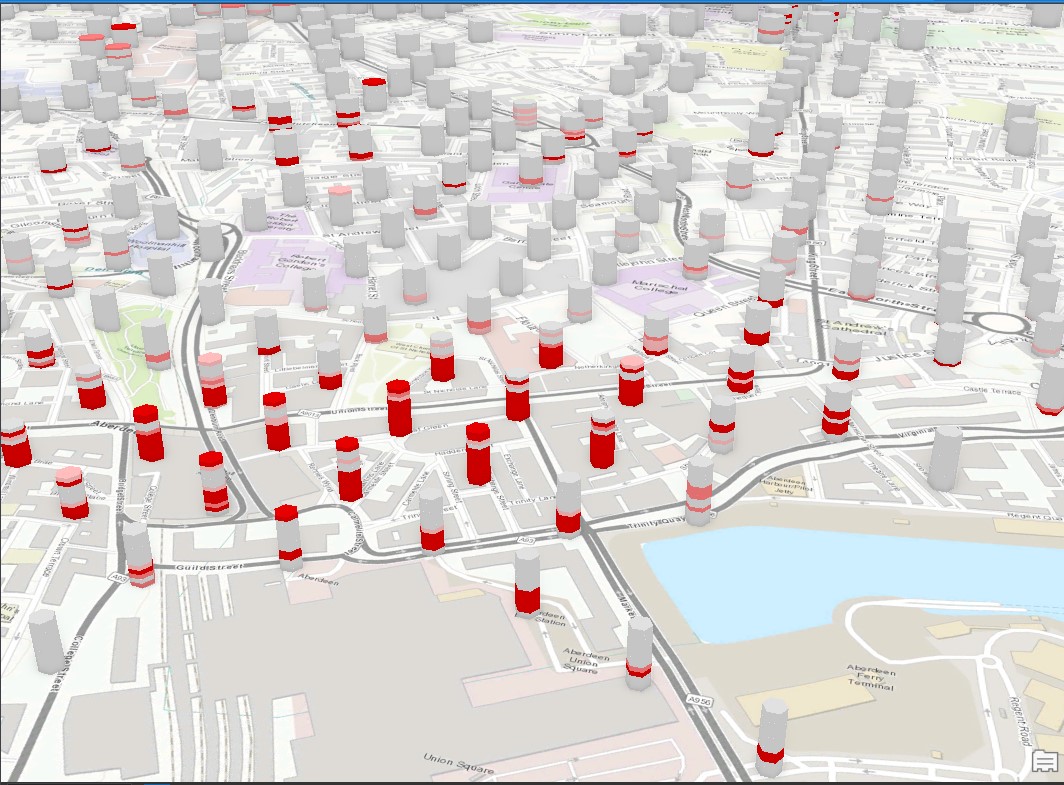 3D Visualization of the Space-Time Cubes
3D Visualization of the Space-Time Cubes -
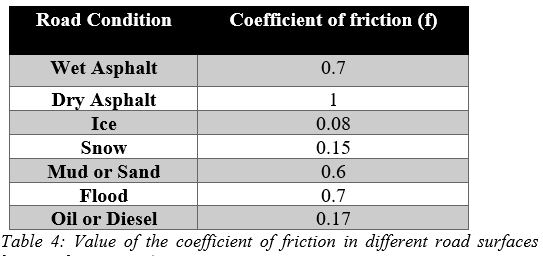
Stopping Sight Distance (SSD) The distance needed for a vehicle to stop before colliding with something in the roadway \(SSD=(0.278*t*V)+V^2/(254*(f + G)\)
where:
\(SSD = Stopping\;Sight\;Distance\) \(t: Reaction\;Time\;in\;Seconds ≃ 1.5\;sec\) \(V: Car\;Speed\;in\;km/h ≃ road’s\;speed\;limit\) \(G: Slope\;level = 0\)
\(f: Coefficient\;of\;friction\)
3. Accident Analysis
Results
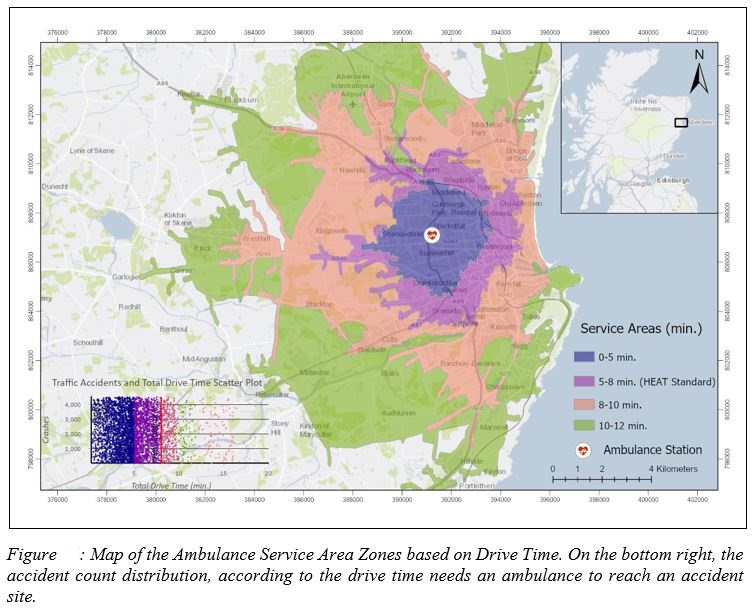
- Ambulance Service Areas and Find Closest Facilities Layers
The Ambulance Service Areas Layer shows the regions that an ambulance can reach within different time-step intervals. In other words, it refers to the time needed for an ambulance to reach the accident location and depends on the network complexity and the road speed limit.
- Space-time Hot Spot Analysis
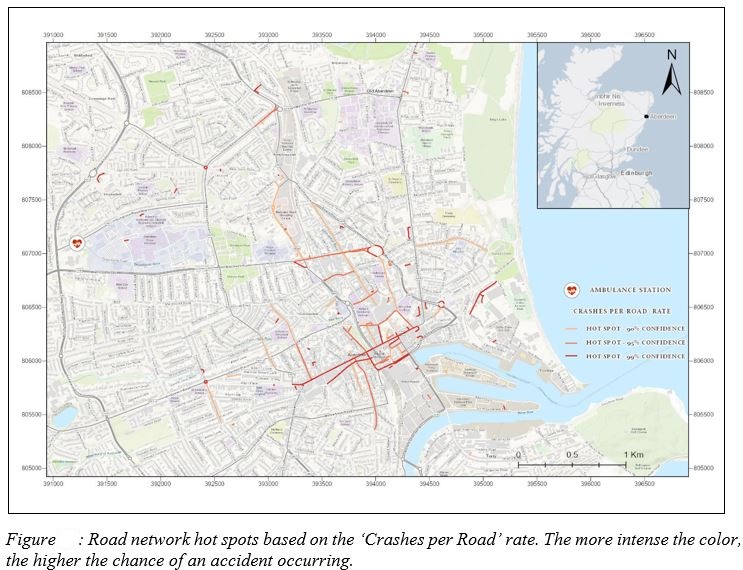
- Accident Rates per Road
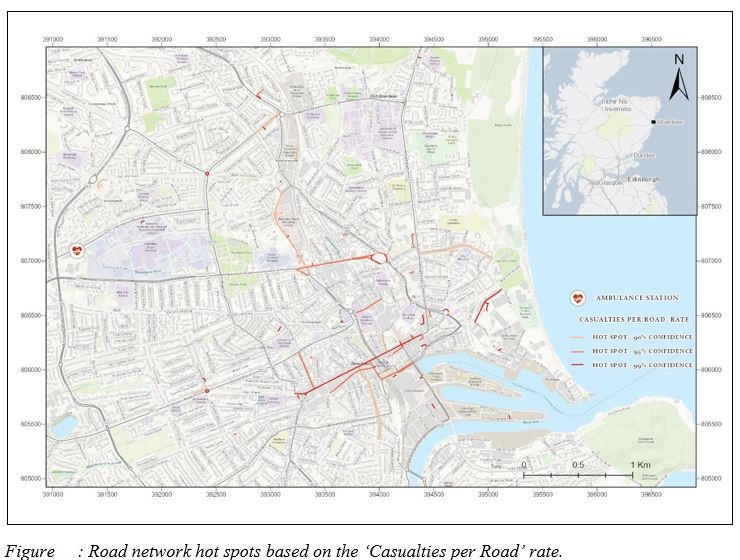
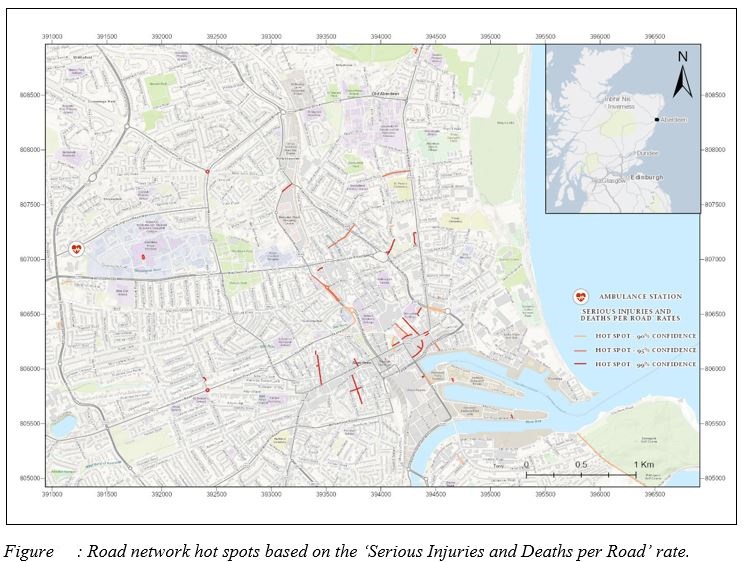
- Accident hot spots comparison
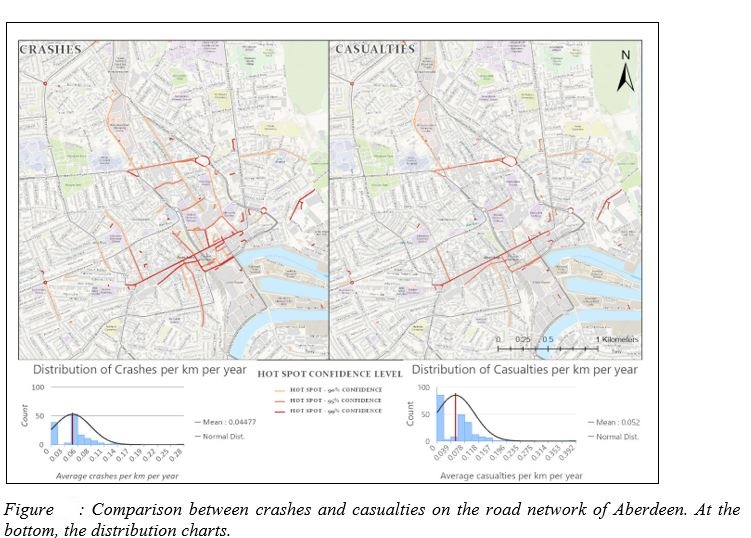
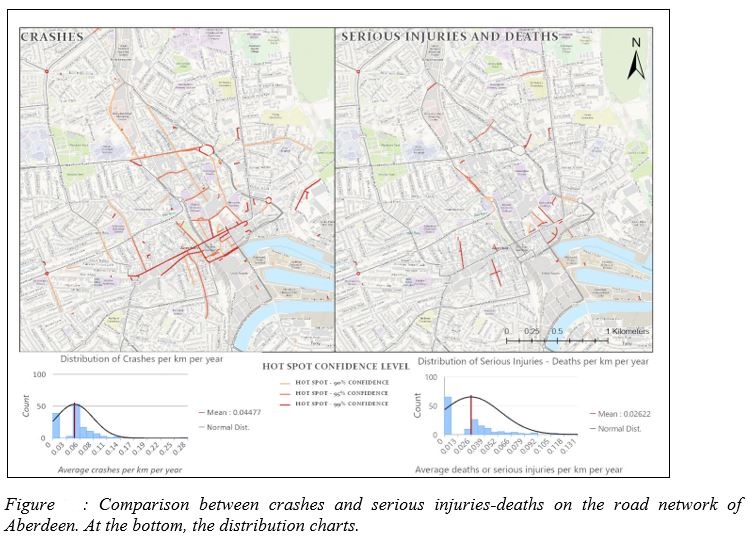
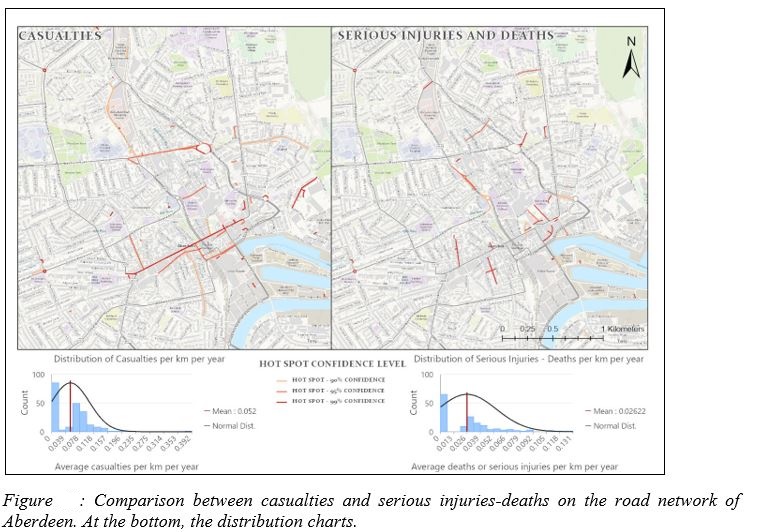
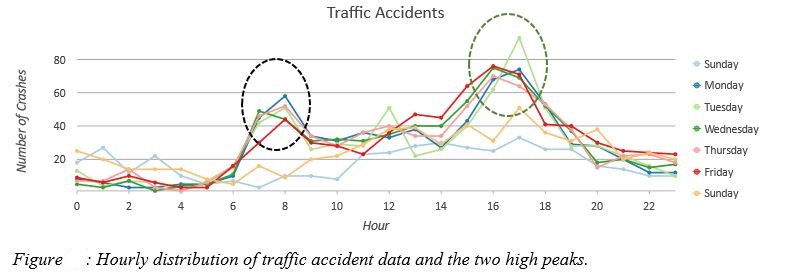
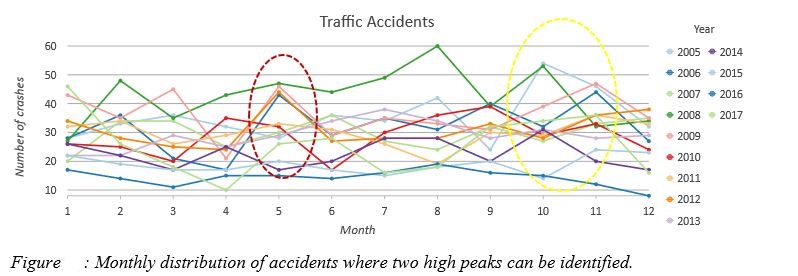
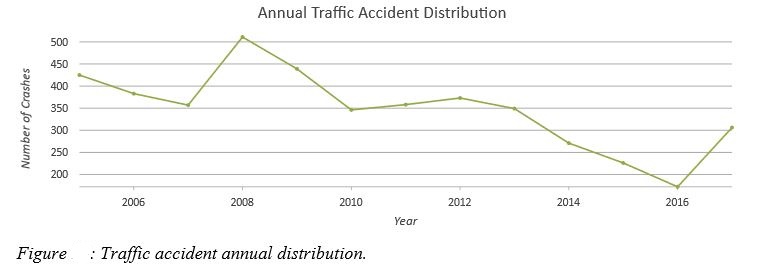
- Temporal Distributions
- Accident Hot Spots and EMS Service Areas Comparison